2020 Practice Exam 1 MCQ Corrections
Final Score 60/67
Q14:
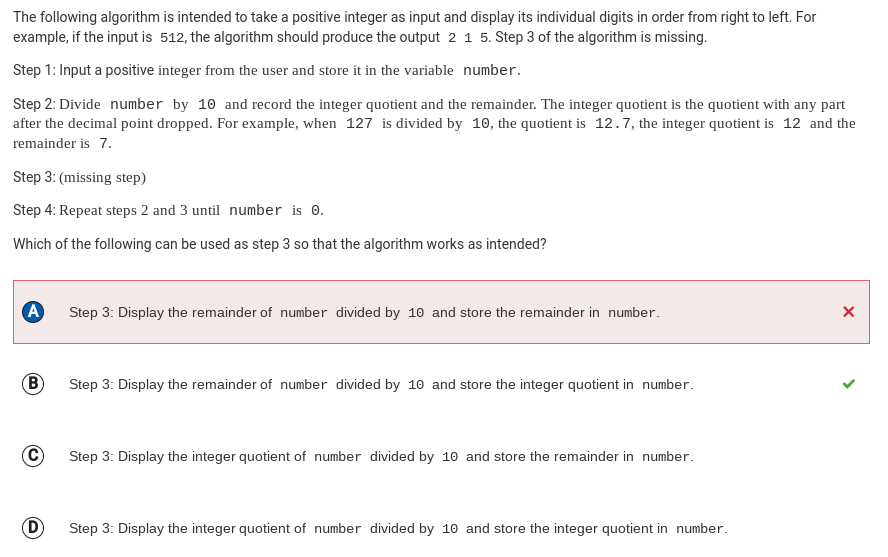
Correction: With this step, the algorithm will result in an infinite loop (unless number is a multiple of 10). For example, if the input is 512, the algorithm will display the remainder 2, then store 2 in number. The remainder of 2 divided by 10 is also 2, so 2 will be displayed and then stored in number again, and so on. If number is a multiple of 10, the algorithm will display 0 and then terminate.
Q15:
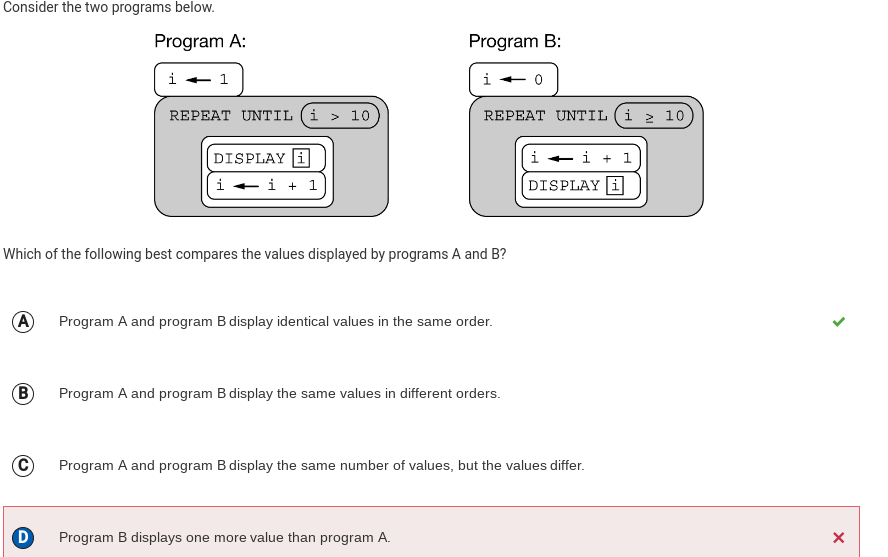
Correction: The answer is A because both programs print ten values.
Q17:
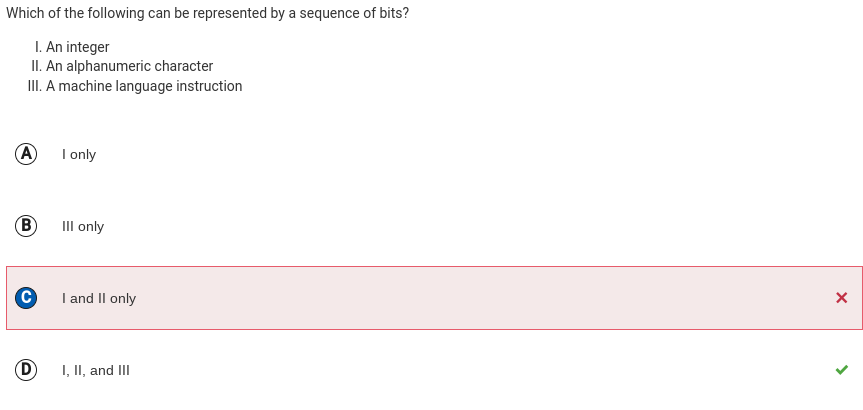
Correction: The answer is D because at the lowest level, all digital data (including machine language instructions) are represented with sequences of bits.
Q32:
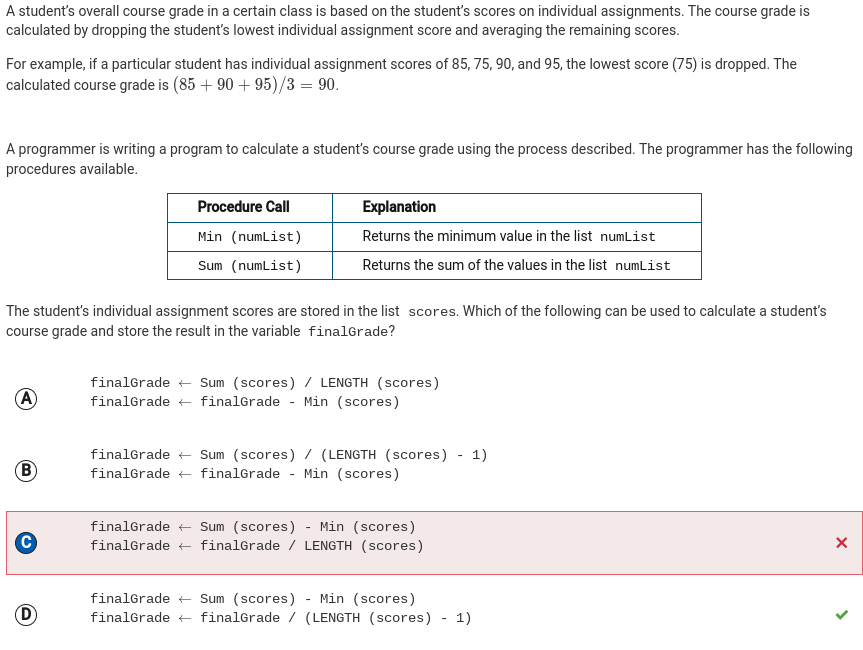
Correction: The answer is D because this code segment subtracts the lowest score from the sum. It erroneously divides this result by the number of scores rather than one less than the number of scores.
Q50:
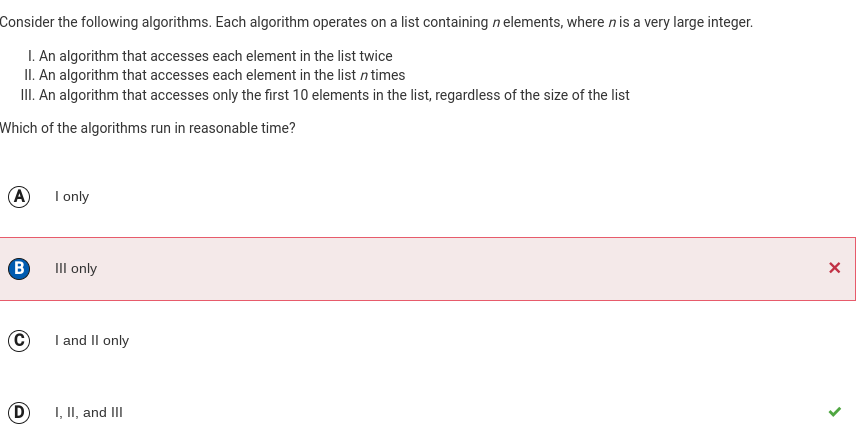
Correction: The answer is D because Algorithm I accesses elements 2n times (twice for each of n elements), which is considered reasonable time. Algorithm II accesses n2 elements (n times for each of n elements), which is considered reasonable time.
Q62:
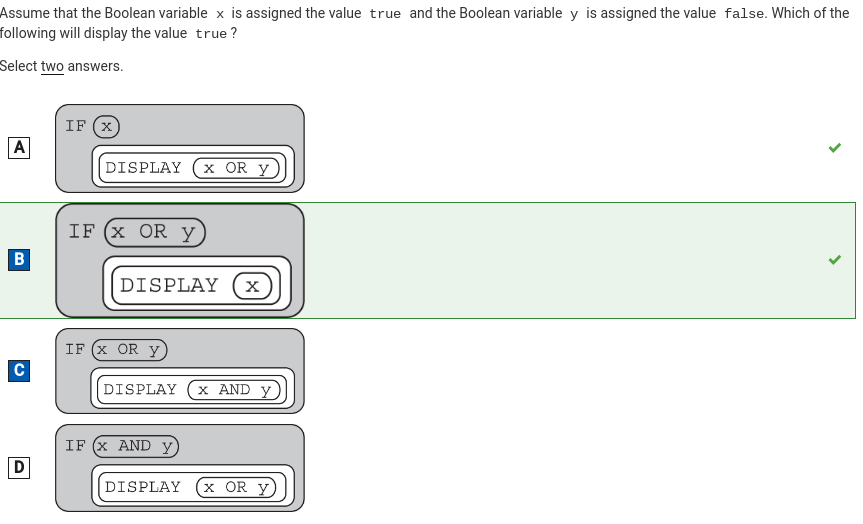
Correction: The answer is A and B rather than B and C because Since x OR y evaluates to true, the body of the IF statement is executed. Since x is true, true is displayed.
Q67:
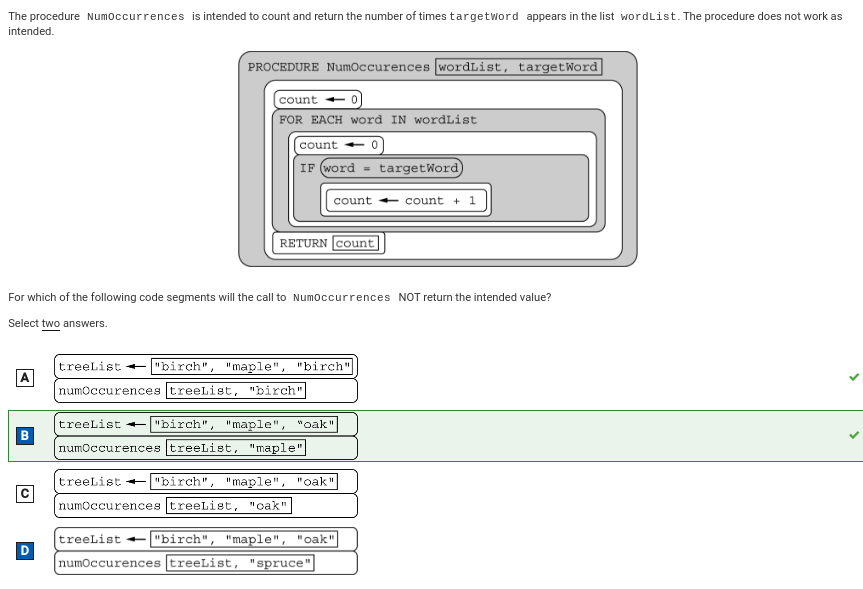
Correction: For this code segment, count is increased to 1 the first time “maple” is encountered in the list. However, count is reset to 0 when the code segment moves to the next list element. This causes the procedure to return 0 instead of the intended result 1.